
About Lesson
Common Types of Networks
Compare the characteristics of common types of networks.

- Small Home Networks – connect a few computers to each other and the Internet
- Small Office/Home Office (SOHO)– enables computer within a home or remote office to connect to a corporate network
- Medium to Large Networks – many locations with hundreds or thousands of interconnected computers
- World Wide Networks – connects hundreds of millions of computers world-wide – such as the internet
LANs and WANs
Network infrastructures vary greatly in terms of:
- Size of the area covered
- Number of users connected
- Number and types of services available
- Area of responsibility
Two most common types of networks:
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)

- A LAN is a network infrastructure that spans a small geographical area.

- A WAN is a network infrastructure that spans a wide geographical area.
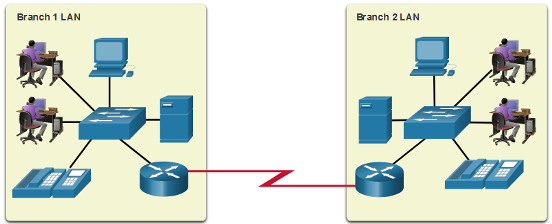
| Network Type | Description |
|---|---|
| LAN (Local Area Network) | Interconnect end devices in a limited area. Administered by a single organization or individual. Provide high-speed bandwidth to internal devices. |
| WAN (Wide Area Network) | Interconnect LANs over wide geographical areas. Typically administered by one or more service providers. Typically provide slower speed links between LANs. |
The Internet
The internet is a worldwide collection of interconnected LANs and WANs.
- LANs are connected to each other using WANs.
- WANs may use copper wires, fiber optic cables, and wireless transmissions.

- The internet is not owned by any individual or group. The following groups were developed to help maintain structure on the internet:
- IETF
- ICANN
- IAB
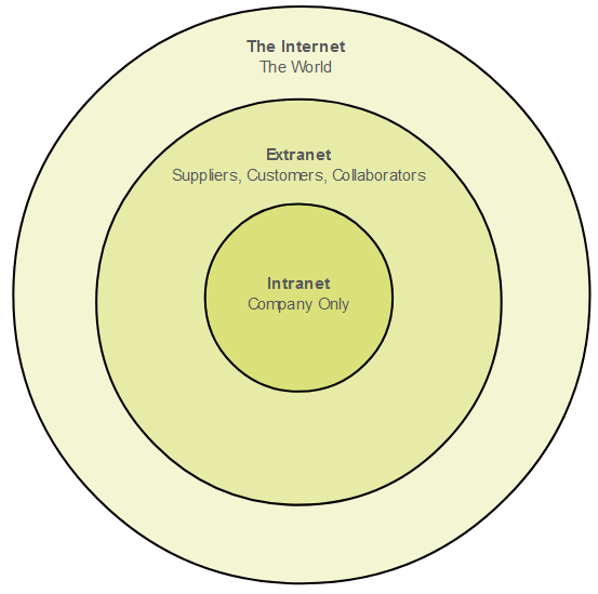
Intranets and Extranets
An intranet is a private collection of LANs and WANs internal to an organization that is meant to be accessible only to the organizations members or others with authorization. An organization might use an extranet to provide secure access to their network for individuals who work for a different organization that need access to their data on their network.
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
| Network Components | Explain how host and network devices are used. |
| Network Representations and Topologies | Explain network representations and how they are used in network topologies. |
| Common Types of Networks | Compare the characteristics of common types of networks. |
| Internet Connections | Explain how LANs and WANs interconnect to the internet. |
| Reliable Networks | Describe the four basic requirements of a reliable network. |
| Network Trends | Explain how trends such as BYOD, online collaboration, video, and cloud computing are changing the way we interact. |
| Network Security Basic | Identify some basic security threats and solution for all networks. |
Other useful information
Join the conversation