
Application, Presentation, and Session
Explain how the functions of the application layer, presentation layer, and session layer work together to provide network services to end user applications.
Application Layer
The upper three layers of the OSI model (application, presentation, and session) define functions of the TCP/IP application layer. The application layer provides the interface between the applications used to communicate, and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted. Some of the most widely known application layer protocols include HTTP, FTP, TFTP, IMAP and DNS. 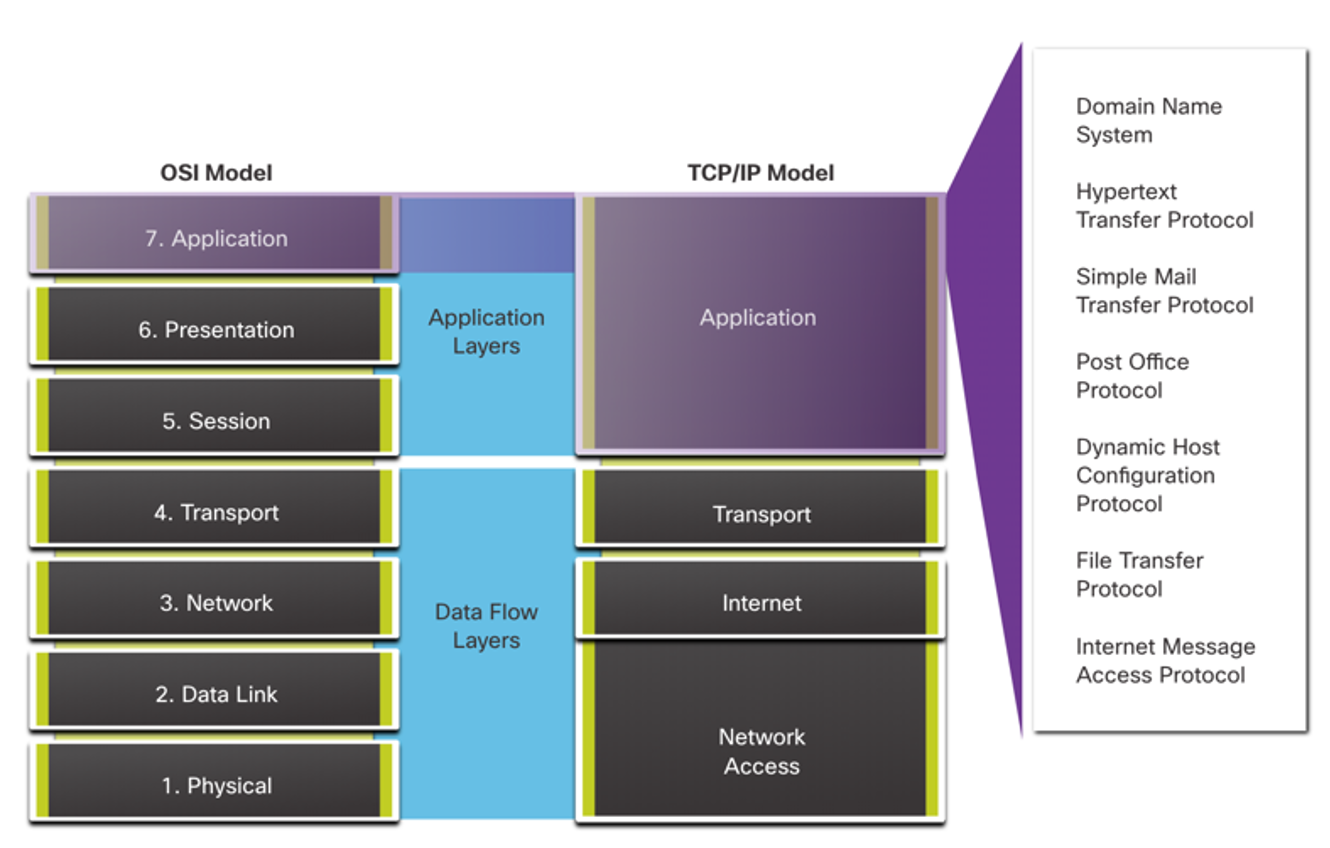
Presentation and Session Layer
The presentation layer has three primary functions:
- Formatting, or presenting, data at the source device into a compatible format for receipt by the destination device
- Compressing data in a way that can be decompressed by the destination device
- Encrypting data for transmission and decrypting data upon receipt
 The session layer functions:
The session layer functions:
- It creates and maintains dialogs between source and destination applications.
- It handles the exchange of information to initiate dialogs, keep them active, and to restart sessions that are disrupted or idle for a long period of time.
TCP/IP Application Layer Protocols
The TCP/IP application protocols specify the format and control information necessary for many common internet communication functions. Application layer protocols are used by both the source and destination devices during a communication session. For the communications to be successful, the application layer protocols that are implemented on the source and destination host must be compatible.
- Name System DNS – Domain Name System (or Service)
-
- TCP, UDP client 53
- Translates domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Host Config DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
-
- UDP client 68, server 67
- Dynamically assigns IP addresses to be re-used when no longer needed
- Web HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol
-
- TCP 80, 8080
- A set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the World Wide Web
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Application, Presentation, and Session | Explain how the functions of the application layer, presentation layer, and session layer work together to provide network services to end user applications. |
| Peer-to-Peer | Explain how end user applications operate in a peer-to-peer network. |
| Web and Email Protocols | Explain how web and email protocols operate. |
| IP Addressing Services | Explain how DNS and DHCP operate. |
| File Sharing Services | Explain how file transfer protocols operate. |