
Network Components
Explain how host and network devices are used.
Host Roles
Every computer on a network is called a host or end device. Servers are computers that provide information to end devices:
- email servers
- web servers
- file server
Clients are computers that send requests to the servers to retrieve information:
- web page from a web server
- email from an email server

| Server Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Email server runs email server software. Clients use client software to access email. | |
| Web | Web server runs web server software. Clients use browser software to access web pages. |
| File | File server stores corporate and user files. The client devices access these files. |
Peer-to-Peer
It is possible to have a device be a client and a server in a Peer-to-Peer Network. This type of network design is only recommended for very small networks.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Easy to set up | No centralized administration |
| Less complex | Not as secure |
| Lower cost | Not scalable |
| Used for simple tasks: transferring files and sharing printers | Slower performance |
End Devices
An end device is where a message originates from or where it is received. Data originates with an end device, flows through the network, and arrives at an end device. 
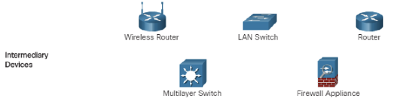
Intermediary Network Devices
An intermediary device interconnects end devices. Examples include switches, wireless access points, routers, and firewalls. Management of data as it flows through a network is also the role of an intermediary device, including:
- Regenerate and retransmit data signals.
- Maintain information about what pathways exist in the network.
- Notify other devices of errors and communication failures.
Network Media
Communication across a network is carried through a medium which allows a message to travel from source to destination. 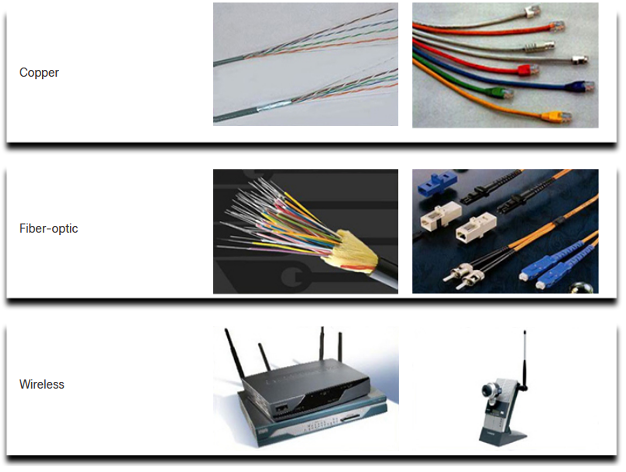
| Media Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Metal wires within cables | Uses electrical impulses |
| Glass or plastic fibers within cables (fiber-optic cable) | Uses pulses of light |
| Wireless transmission | Uses modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves |
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
| Network Components | Explain how host and network devices are used. |
| Network Representations and Topologies | Explain network representations and how they are used in network topologies. |
| Common Types of Networks | Compare the characteristics of common types of networks. |
| Internet Connections | Explain how LANs and WANs interconnect to the internet. |
| Reliable Networks | Describe the four basic requirements of a reliable network. |
| Network Trends | Explain how trends such as BYOD, online collaboration, video, and cloud computing are changing the way we interact. |
| Network Security Basic | Identify some basic security threats and solution for all networks. |