
About Lesson
Network Segmentation
Explain how subnetting segments a network to enable better communication.
Broadcast Domains and Segmentation
- Many protocols use broadcasts or multicasts (e.g., ARP use broadcasts to locate other devices, hosts send DHCP discover broadcasts to locate a DHCP server.) Switches propagate broadcasts out all interfaces except the interface on which it was received.

- The only device that stops broadcasts is a router. Routers do not propagate broadcasts. Each router interface connects to a broadcast domain and broadcasts are only propagated within that specific broadcast domain.
Problems with Large Broadcast Domains
- A problem with a large broadcast domain is that these hosts can generate excessive broadcasts and negatively affect the network.

- The solution is to reduce the size of the network to create smaller broadcast domains in a process called subnetting. Dividing the network address 172.16.0.0 /16 into two subnets of 200 users each: 172.16.0.0 /24 and 172.16.1.0 /24.
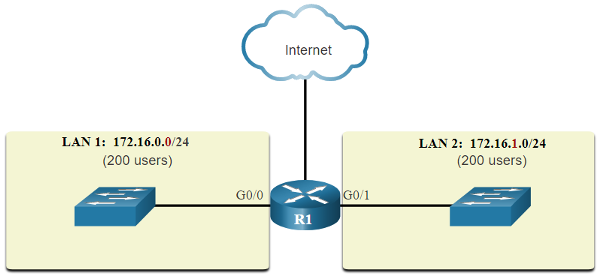
- Broadcasts are only propagated within the smaller broadcast domains.
Reasons for Segmenting Networks
- Subnetting reduces overall network traffic and improves network performance. It can be used to implement security policies between subnets. Subnetting reduces the number of devices affected by abnormal broadcast traffic.
- Subnets are used for a variety of reasons including by:
- Location
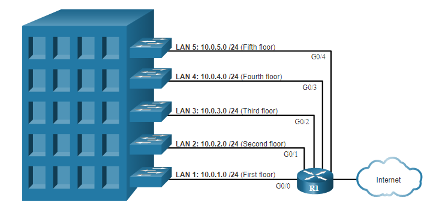
-
- Group or Function

-
- Device Type
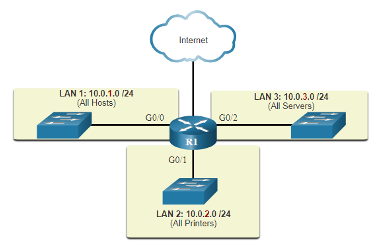
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address Structure | Describe the structure of an IPv4 address including the network portion, the host portion, and the subnet mask. |
| IPv4 Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast | Compare the characteristics and uses of the unicast, broadcast, and multicast IPv4 addresses. |
| Types of IPv4 Addresses | Explain public, private, and reserved IPv4 addresses. |
| Network Segmentation | Explain how subnetting segments a network to enable better communication. |
| Subnet an IPv4 Network | Calculate IPv4 subnets for a /24 prefix. |
| VLSM | Variable length subnet mask is a computer networking technique to divide an IP network into subnets with different subnet masks |
Other useful information
Join the conversation