
Fibre Channel Storage
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Describe uses of Fibre Channel with ESXi
- Identify Fibre Channel components and addressing
- Explain how multipathing with Fibre Channel works
About Fibre Channel
 Fibre Channel stores VM files remotely on a Fibre Channel SAN.
Fibre Channel stores VM files remotely on a Fibre Channel SAN.
A Fibre Channel SAN is a specialized highspeed network that connects your hosts to highperformance storage devices.
The network uses the Fibre Channel protocol to transport SCSI traffic from VMs to the Fibre Channel SAN devices. ESXi supports:
- 32 Gbps Fibre Channel
- Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)
Fibre Channel SAN Components
A SAN consists of one or more servers that are attached to a storage array using one or more SAN switches.

Fibre Channel Addressing and Access Control

Multipathing with Fibre Channel
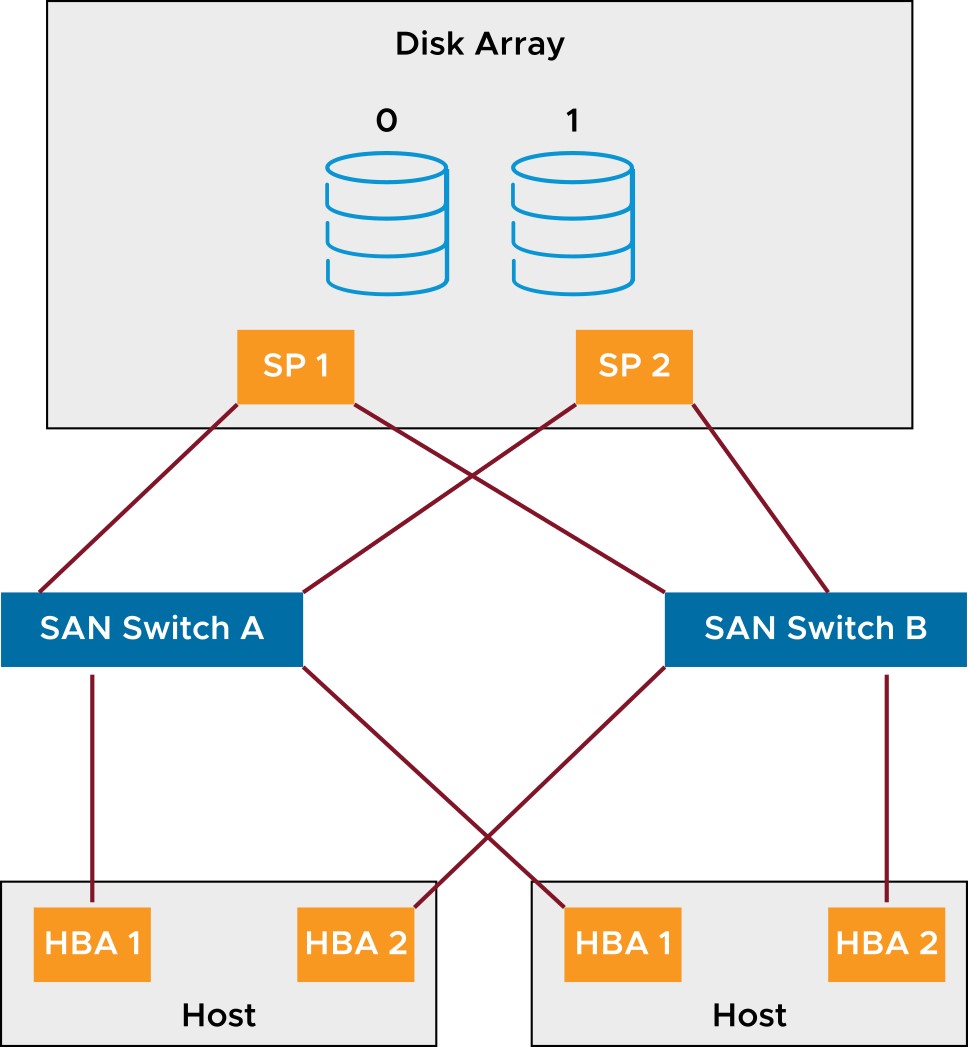
Multipathing is having more than one path from a host to a LUN. Multipathing provides the following functions:
- Continued access to SAN LUNs if hardware fails
- Load balancing
FCoE Adapters
If your host contains FCoE adapters, you can connect to your shared Fibre Channel devices by using an Ethernet network. 
Configuring Software FCoE: Creating VMkernel Ports

- Step 1: Connect the VMkernel to the physical FCoE NICs that are installed on your host:
- The VLAN ID and the priority class are discovered during FCoE initialization. The priority class is not configured in vSphere.
- ESXi supports a maximum of four network adapter ports for software FCoE.
Configuring Software FCoE: Activating Software FCoE Adapters
- Step 2: Add the software FCoE adapter and configure it as needed.

Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this Fibre Channel Storage lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Describe uses of Fibre Channel with ESXi
- Identify Fibre Channel components and addressing
- Explain how multipathing with Fibre Channel works