
Monitoring Resource Use in vSphere
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Monitor the key factors that can affect a virtual machine’s performance
- Use performance charts to view and improve performance
Interpreting Data from Tools vCenter Server monitoring tools and guest OS monitoring tools provide different points of view. 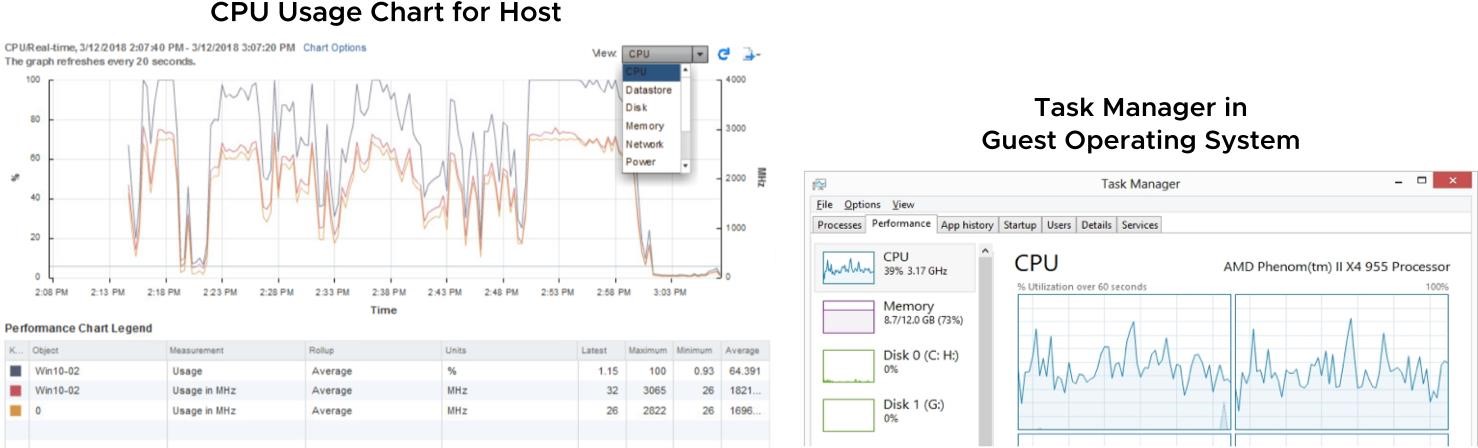
CPU-Constrained VMs (1)
If CPU use is continuously high, the VM is constrained by the CPU. However, the host might have enough CPU for other VMs to run.

CPU-Constrained VMs (2)
Multiple VMs are constrained by the CPU if the following conditions are present:
- High CPU usage in the guest operating system
- Relatively high CPU readiness values for the VMs

Memory-Constrained VMs (1)
Compare a VM’s memory consumed and granted values to determine whether the VM is memory-constrained.

Memory-Constrained VMs (2)
If a VM consumes its entire memory allocation, the VM might be memory-constrained, and you should consider increasing the VM’s memory size. 
Memory-Constrained Hosts
Any evidence of ballooning or swapping is a sign that your host might be memory-constrained.

Disk-Constrained VMs
Disk-intensive applications can saturate the storage or the path. If you suspect that a VM is constrained by disk access, take these actions:
- Measure the throughput and latency between the VM and storage.
- Use the advanced performance charts to monitor throughput and latency:
- Read rate and write rate
- Read latency and write latency
Monitoring Disk Latency
To determine disk performance problems, monitor two disk latency data counters:
- Kernel command latency:
- This counter is the average time that is spent in the VMkernel per SCSI command.
- High numbers (greater than 2 milliseconds or 3 milliseconds) represent either an overworked array or an overworked host.
- Physical device command latency:
- This counter is the average time that the physical device takes to complete a SCSI command.
- High numbers represent a slow or overworked array, for example:
- For spinning disks (HDDs), greater than 15 milliseconds or 20 milliseconds
- For SSDs, greater than 3 milliseconds or 4 milliseconds
Network-Constrained VMs
Network-intensive applications often bottleneck on path segments outside the ESXi host:
- Example: WAN links between server and client
If you suspect that a VM is constrained by the network, take these actions:
- Verify that VMware Tools is installed and that VMXNET3 is the virtual network adapter.
- Measure the effective bandwidth between the VM and its peer system.
- Check for dropped receive packets and dropped transmit packets.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this Monitoring Resource Use in vSphere lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Monitor the key factors that can affect a virtual machine’s performance
- Use performance charts to view and improve performance