
vSphere HA Architecture
Learner Objectives
After completing this vSphere HA Architecture lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Identify the heartbeat mechanisms used by vSphere HA
- Describe failure scenarios
- Recognize vSphere HA design considerations
vSphere HA Architecture: Agent Communication
When vSphere HA is enabled in a cluster, the Fault Domain Manager (FDM) service starts on the hosts in the cluster.

vSphere HA Architecture: Network Heartbeats
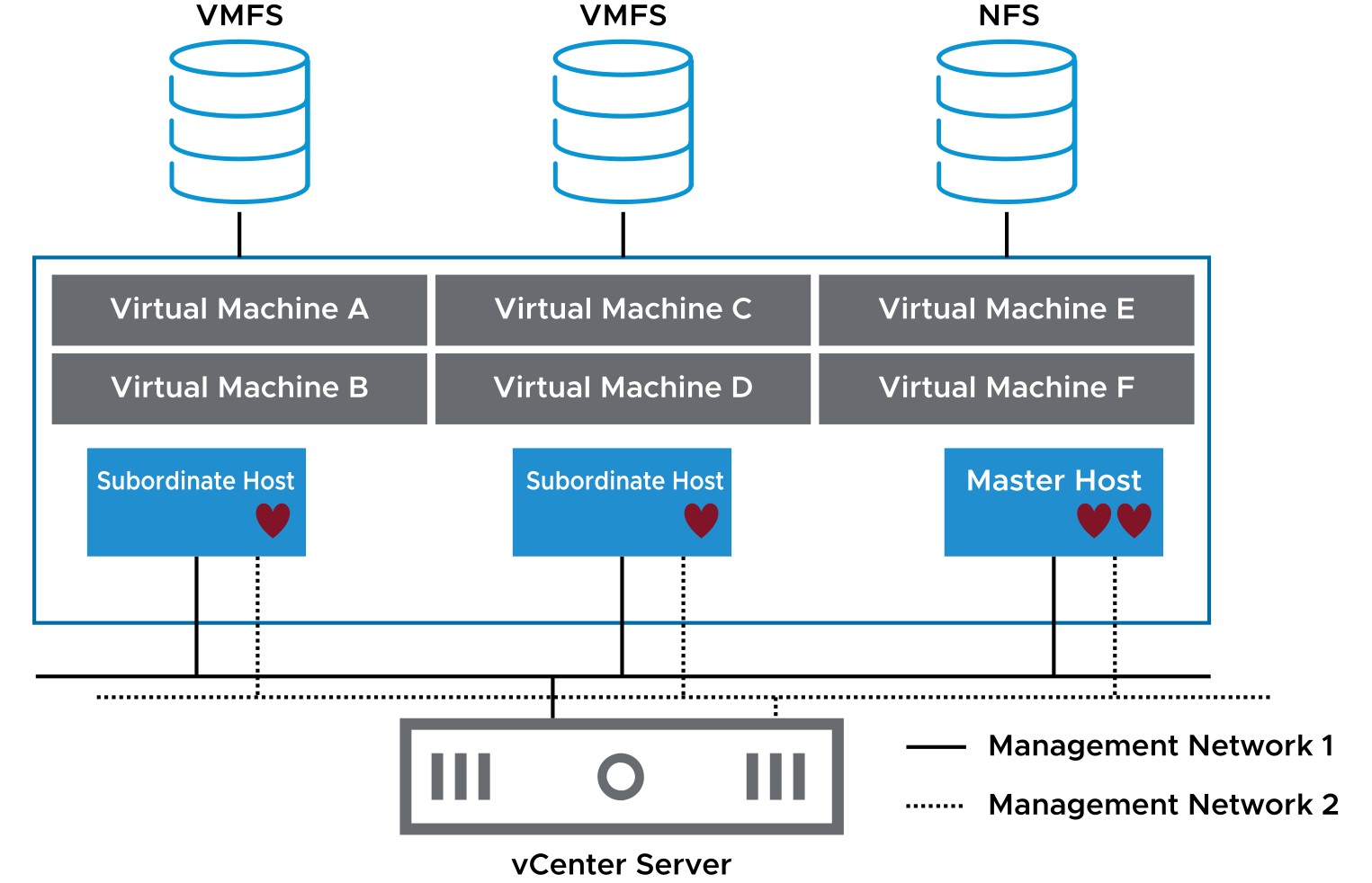
The master host sends periodic heartbeats to the subordinate hosts. In this way, the subordinate hosts know that the master host is alive and the master host knows that the subordinate hosts are alive.
vSphere HA Architecture: Datastore Heartbeats
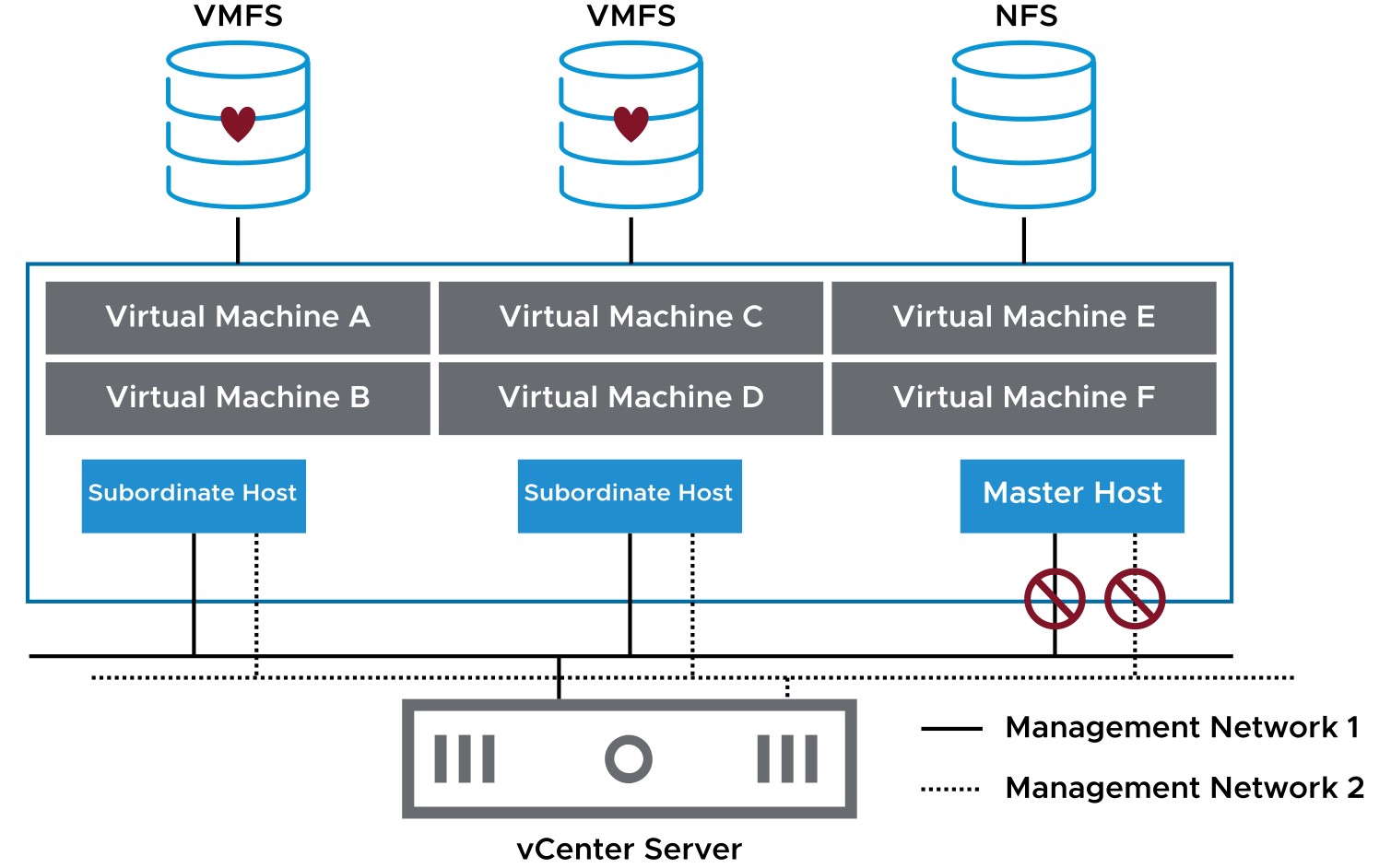
When the master host cannot communicate with a subordinate host over the management network, the master host uses datastore heartbeating to determine the cause:
- Subordinate host failure
- Network partition
- Network isolation
vSphere HA Failure Scenarios
vSphere HA can identify and respond to various types of failures:
- Subordinate host failure
- Master host failure
- Network failure (host isolation)
VMCP enables vSphere HA to detect and respond to datastore access failures:
- APD
- PDL
Failed Subordinate Hosts
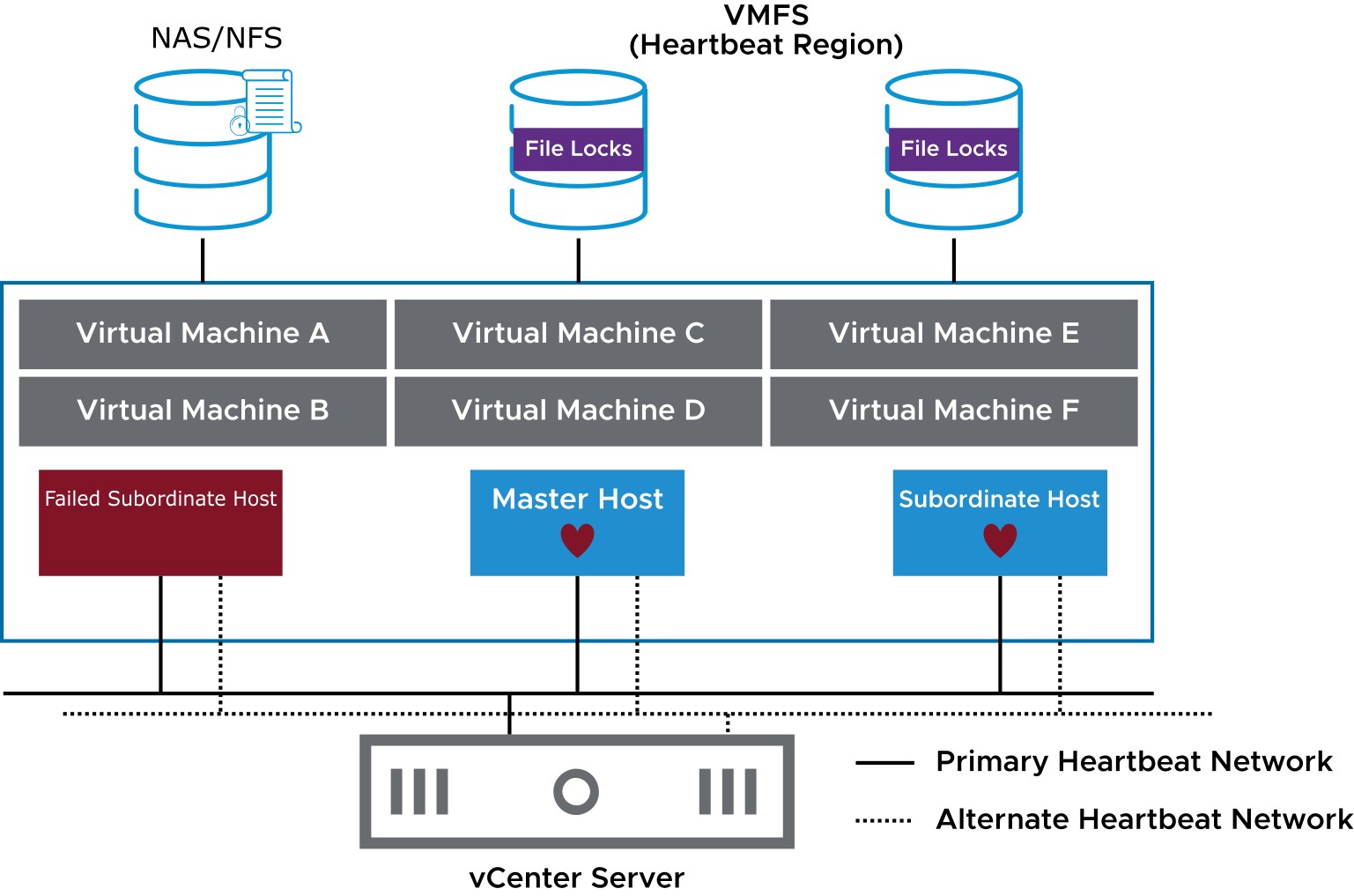
When a subordinate host does not respond to the network heartbeat issued by the master host, the master host tries to identify the cause.
Failed Master Hosts

When the master host is placed in maintenance mode or fails, the subordinate hosts detect that the master host is no longer issuing heartbeats.
Isolated Hosts

A host is declared isolated when the following conditions occur:
- The host is not receiving network heartbeats.
- The host cannot ping its isolation addresses.
VM Storage Failures

Storage connectivity problems might arise because of:
- Network or switch failure
- Array misconfiguration
- Power outage
Storage connectivity problems affect VM availability:
- VMs on affected hosts are difficult to manage.
- Applications with attached disks fail.
Protecting Against Storage Failures with VMCP
VM Component Protection protects against storage failures on a VM.
- If VMCP is enabled, vSphere HA can detect datastore accessibility failures and provide automated recovery for affected VMs.
- VMCP is not supported with vSAN.

vSphere HA Design Considerations
When designing your vSphere HA cluster, consider these guidelines:
- Implement redundant heartbeat networks and redundant isolation addresses:
- Redundancy minimizes host isolation events.
- Physically separate VM networks from the heartbeat networks.
- Implement datastores so that they are separated from the management network by using one or both of the following approaches:
- Use Fibre Channel over fiber optic for your datastores.
- If you use IP storage, physically separate your IP storage network from the management network.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this vSphere HA Architecture lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Identify the heartbeat mechanisms used by vSphere HA
- Describe failure scenarios
- Recognize vSphere HA design considerations